US DATA: Productivity Just Strong Enough To Subdue Labor Inflation Impact (2/2)
Feb-06 15:55
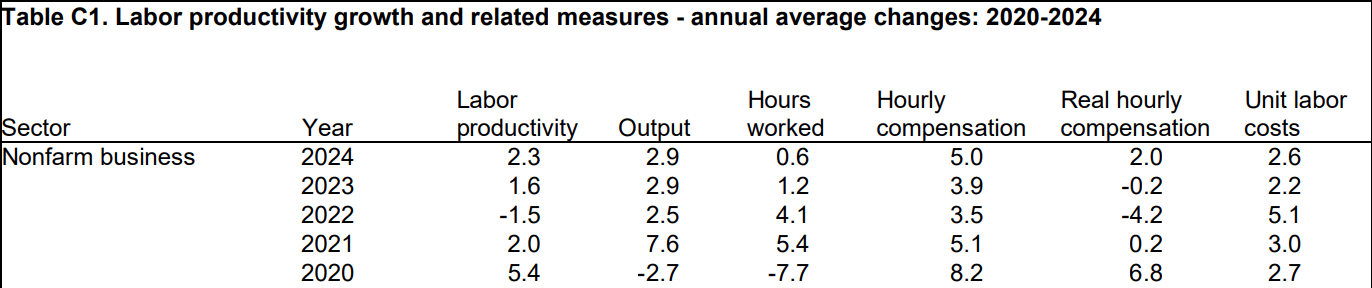
Large revisions are a constant theme in the productivity/ULC series, so they are best considered in terms of longer-term trends.
- In 2024, nonfarm business productivity rose 2.3% on an annual average basis (output up 2.9%, hours worked up 0.6%), with ULCs up 2.6% (5.0% rise in hourly compensation, 2.3% rise in productivity). The table below shows that while productivity picked back up in 2024 to a 4-year high, offsetting a 3-year high for hourly compensation.
- The 5-year average for productivity growth is 2.0%, while hourly compensation rose 5.1%, which means unit labor costs have risen by 3.1%.
- Of course the picture of recent history could be altered radically by the benchmark revisions to the BLS employment data out Friday, because the expected drop in the level of employment to early 2024 would mechanically increase the implied growth in productivity. We will get confirmation of this in the productivity revisions due March 6.
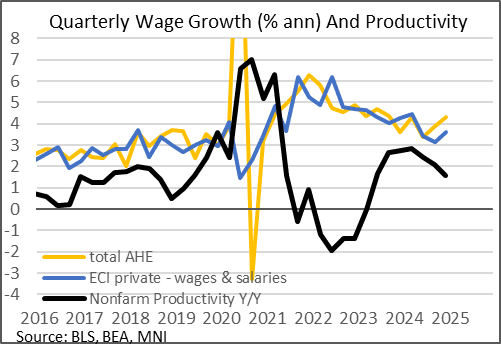
- As it stands, from the perspective of the 2% inflation target, with productivity remaining at 2.0%, wage growth of 4% would be consistent with hitting the target.
- Wage growth is close to that now: the Q4 Employment Cost Index was 3.6% Q/Q annualized in Q4 2024, with average hourly earnings up 4.3% annualized at the end of last year (3.9% Y/Y).
- A slowdown in productivity to 1.5-2.0% - where landed in Q4 2024 - is probably too low to be consistent with bringing inflation down to the 2% target, and a recent uptick in AHE and ECI on an annualized basis bears attention.
- But the longer-term view (let alone prospects of a pickup in productivity amid advancements like AI) will probably keep Fed policymakers at least cautiously optimistic on the labor market's impact on inflation - even before potential upward productivity revisions.
Want to read more?
Find more articles and bullets on these widgets:
Historical bullets
US DATA: Softer Hires Rate Chimes With Lower Quits
Jan-07 15:49
- Returning to the JOLTS report, hiring details were also on the soft side, chiming more with the resumed downtrend for quits rates than the stronger than expected job openings.
- The hires rate fell to 3.31% in Nov from 3.39% in Oct and 3.51% in Sept, drawing level with the 3.31% in June that marked the lowest since Apr 2020 and before that late 2013.

GILT AUCTION PREVIEW: On offer next week
Jan-07 15:46
The DMO has announced it will be looking to sell GBP1bln of the 1.25% Nov-54 linker (ISIN: GB00BPSNBG80) at its auction next Tuesday, January 14.
EGB SYNDICATION: New 30-year SLOREP: Priced
Jan-07 15:36
- Size set earlier: E1bln (MNI had expected E1.0-1.5bln)
- Spread set earlier at MS+128 (Guidance was MS+140bps area then MS+135bps area)
- Reoffer price 99.10 to yield 3.548%
- Benchmark: DBR 2.5% 08/15/54 +85.1
- Books above EU2.1b (including JLM interest)
- Maturity date: 14 April 2055
- Coupon: 3.5%, annual, act/act, long first
- Issuer: Slovenia Government Bond (SLOREP)
- Settlement: 14 January 2025 (T+5)
- ISIN: SI0002104873
- Joint bookrunners: Deutsche Bank, Erste Group, Goldman Sachs Bank Europe SE, HSBC, J.P. Morgan (B&D), and OTP Banka Slovenia
- Timing: 3:20pm London
Details as per Bloomberg and Market Source